New Journal of Physics 18 075014 (2016)
P. Navez, S. Pandey, H. Mas, K. Poulios, T. Fernholz, and W. von Klitzing
doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/18/7/075014
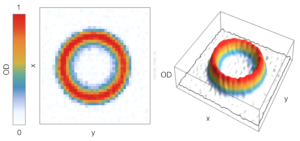
Figure 2. Experimental realisation of a ring-shaped TAAP waveguide. The radius of the ring is R = 570 μm.
Abstract: We present two novel matter-wave Sagnac interferometers based on ring-shaped time-averaged adiabatic potentials, where the atoms are put into a superposition of two different spin states and manipulated independently using elliptically polarized rf-fields. In the first interferometer the atoms are accelerated by spin-state-dependent forces and then travel around the ring in a matter-wave guide. In the second one the atoms are fully trapped during the entire interferometric sequence and are moved around the ring in two spin-state-dependent `buckets’.

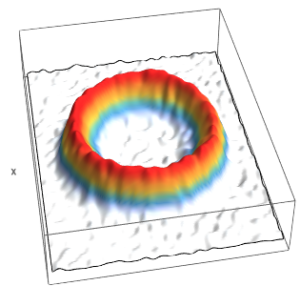
Figure 6. Experimental realisation of arbitrary traps. The fitted radius is 440 μm and 450 μm respectively. Note that (a) and (b) are taken with identical experimental conditions and differ only in the state of the atoms. The axis of the circular rf component and the one of the tilted modulation are not orthogonal.
Corrections to the ideal Sagnac phase are investigated for both cases. We experimentally demonstrate the key atom-optical elements of the interferometer such as the independent manipulation of two different spin states in the ring-shaped potentials under identical experimental conditions.






You must be logged in to post a comment.